News
What are the Functions of the Cable Fault Indicator
Date:2022-12-09
Cable faults Indicator caused by mechanical damage account for a large proportion of cable accidents. According to statistics, the failure rate caused by external mechanical damage is the largest. Some mechanical damage is so minor that it did not cause a failure at the time, but it took months or even years for the damage to develop into a failure. There are mainly the following reasons for the mechanical damage of the cable: damage during installation: accidentally bruising the cable during installation, excessive mechanical traction and straining the cable, or excessive bending of the cable and damage to the cable. Directly damaged by external force: urban construction is carried out on the cable path or near the cable after installation, so that the cable is directly damaged by external force.
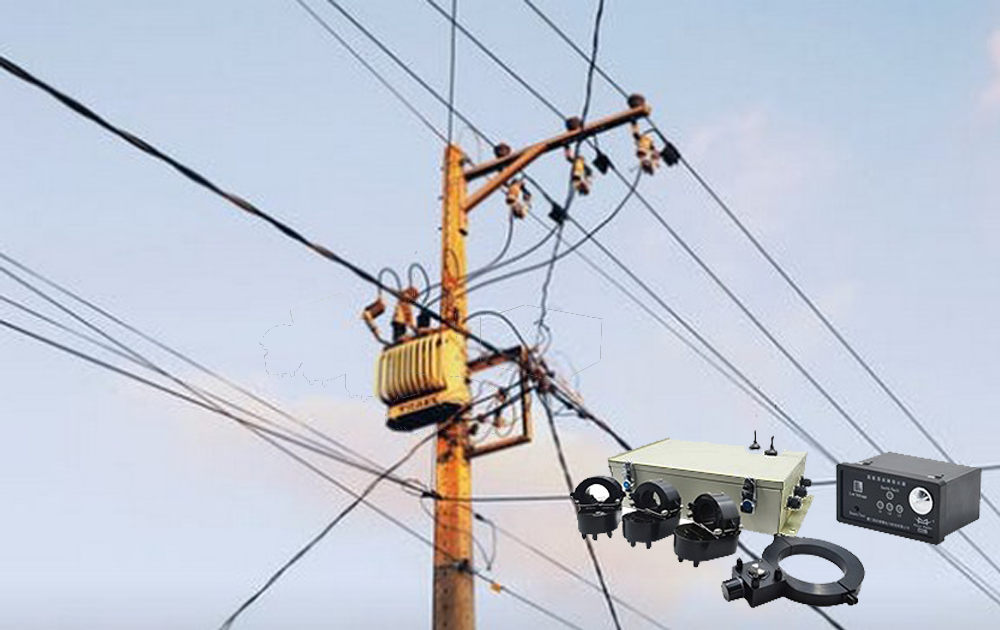

The vibration or impact load of the driving vehicle will cause the lead (aluminum) package of the underground cable to crack. Damage caused by natural phenomena: such as the expansion of the insulating rubber in the intermediate joint or the terminal head and the expansion of the shell or cable sheath; the scratches on the outer skin of the cable installed on the nozzle or bracket due to the natural travel of the cable; excessive damage caused by land subsidence Pulling force, breaking the intermediate joint or conductor. Damage to insulation caused by moisture. The main reasons for the cable to be damp are: water ingress due to unsealed joint box or terminal box structure or poor installation. The cable is poorly made with small holes or cracks in the metal sheath. The metal sheath is pierced by foreign objects or corroded. The air gap inside the cable insulation medium is dissociated under the action of the electric field to reduce the insulation. When the insulating medium is ionized, chemical products such as ozone and nitric acid are produced in the air gap, which corrodes the insulation; the moisture in the insulation causes the insulating fiber to hydrolyze, resulting in a decrease in insulation.
Overheating will cause insulation aging and deterioration. Electric dissociation in the air gap inside the cable causes local overheating and carbonization of the insulation. Cable overloading is a very important factor in cable overheating. Cables installed in cable-intensive areas, cable trenches, cable tunnels and other poorly ventilated places, cables in drying pipes, and parts close to cables and heat pipes will all cause accelerated insulation damage due to their own overheating. The effect of the atmosphere and the internal overvoltage causes the insulation breakdown of the cable to form a fault, and the breakdown point is generally defective. The waterproof design of the intermediate joint and the terminal head, the design of the electric field distribution is not careful, the selection of materials is improper, the workmanship is poor, and the production is not in accordance with the requirements of the regulations, which will cause the failure of the cable head.
Material defects are mainly manifested in three aspects. One is the problem of cable manufacturing, defects left by the lead (aluminum) sheath; during the wrapping insulation process, defects such as folds, cracks, breaks, and overlapping gaps appear on the paper insulation; the second is defects in the manufacture of cable accessories , such as cast iron parts have blisters, the mechanical strength of porcelain parts is not enough, other parts do not meet the specifications or are not sealed when assembled; the third is poor maintenance and management of insulating materials, resulting in moisture, dirt and aging of cable insulation. Due to the influence of underground acid-base corrosion and stray current, the lead sheath of the cable is corroded and pitted, cracked or perforated, resulting in failure. When the oil-impregnated paper insulated cable is laid, the trench is uneven, or the outdoor head on the pole, due to the ups and downs and the great difference in height, the insulating oil in the high place flows to the low place, which reduces the insulation performance of the high-place cable, resulting in failure.
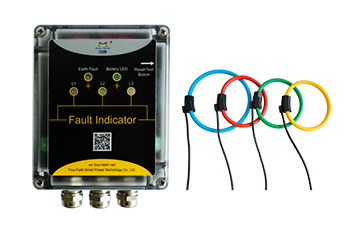
Cable Fault indicators provide a quick way to solve fault finding problems, and are of great significance to improving work efficiency, shortening power outage time, quickly restoring power supply, improving power supply reliability and economic benefits.
The main functions of the cable fault indicator:
1. Short-circuit alarm indication: The short-circuit sensor detects the current of the line during operation. When the short-circuit fault occurs in the line and the current reaches or exceeds the set value of the short-circuit current, the short-circuit sensor sends out an alarm signal, which is transmitted to the host through the optical cable. After the host receives this signal , to generate a corresponding alarm indication signal.
2. Grounding alarm indication: The grounding sensor detects the zero-sequence current of the line during work. When the grounding fault occurs in the line, when the grounding current reaches or exceeds the setting value of the grounding current, the grounding sensor sends out an alarm signal, which is transmitted to the host through the optical cable, and the host receives it. After receiving this signal, a corresponding alarm indication signal is generated.
3. Automatic reset: After the cable fault indicator sends out an alarm signal, if there is no manual reset, the cable fault indicator can automatically reset after a set time.
4. Manual reset: When the cable fault indicator generates an alarm, the alarm can be canceled by pressing the "Reset/Test" button on the panel of the cable fault indicator host for 2 seconds.
5. Automation: After the cable fault indicator generates the corresponding alarm indication signal, the alarm signal can be output to remote transmission. The cable fault indicator can also receive a remote reset signal to perform a remote reset operation on the cable fault indicator.