News
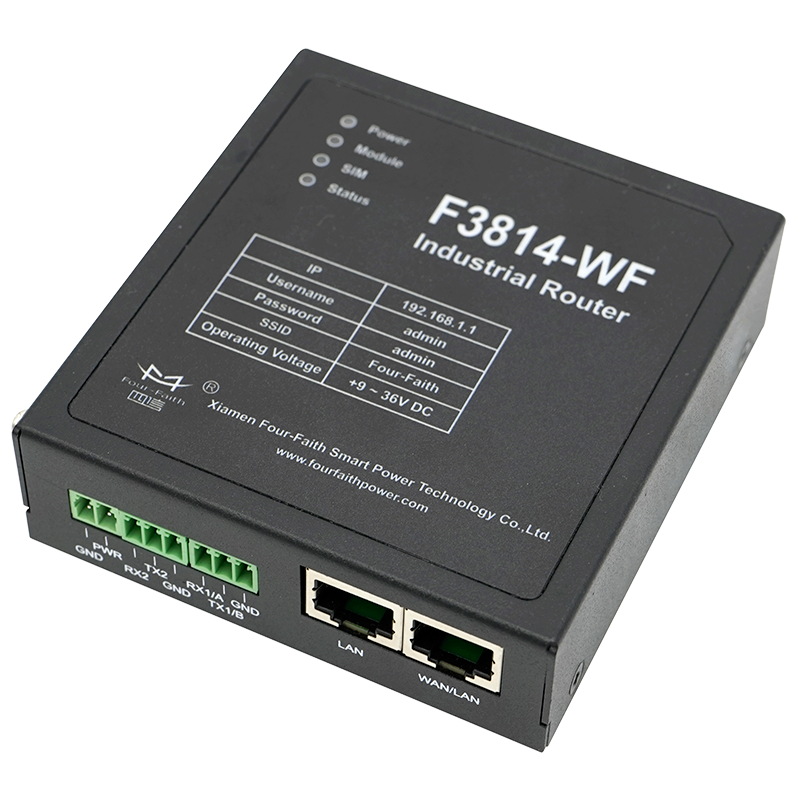
What Is an Industrial Router in power systems ?
Date:2026-01-30
What Is an Industrial Router?
An industrial router is a networking device specifically designed for harsh industrial environments. Compared with commercial routers, industrial routers feature:
- Wide operating temperature ranges
- High resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI)
- Industrial-grade components for long-term stability
- Advanced security and redundancy mechanisms
- In power systems, these characteristics are essential due to high-voltage environments, outdoor installations, and mission-critical communication requirements.
Why Power Systems Need Industrial Routers
Power systems rely heavily on real-time data exchange between substations, control centers, field devices, and distributed energy resources. Any communication failure may result in delayed fault response, system instability, or even large-scale outages.
Industrial routers provide the following key benefits:
1. Reliable Communication in Harsh Environments
Power substations, distribution networks, and renewable energy sites often face extreme temperatures, humidity, vibration, and electrical noise. Industrial routers are designed to operate reliably under these conditions, ensuring uninterrupted communication.
2. Secure Data Transmission
Cybersecurity is a growing concern in modern power grids. Industrial routers support advanced security features such as VPN, firewall, access control, and encryption, protecting critical power system data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Industrial routers enable seamless data transmission for SCADA systems, distribution automation, fault indicators, and power sensors. This real-time connectivity allows utilities to monitor system status, detect faults quickly, and respond efficiently.
4. Flexible Networking Options
Industrial routers support multiple communication methods, including:
- Ethernet
- Fiber optic
- Cellular (4G/5G)
- Serial interfaces
This flexibility makes them suitable for various power system applications, from urban substations to remote distribution networks.
Typical Applications in Power Systems
Industrial routers are widely used across different segments of the power grid:
Substation Automation
Connecting protection relays, RTUs, IEDs, and control systems to central management platforms.
Distribution Automation
Supporting communication for fault detection, isolation, and service restoration (FDIR).
Power Communication Networks
Acting as gateways between field devices and power dispatch centers.
Renewable Energy Integration
Enabling stable communication for solar plants, wind farms, and energy storage systems.
Remote Monitoring
Providing reliable connectivity for unmanned substations and outdoor power equipment.
Key Features to Look for in Power System Industrial Routers
When selecting an industrial router for power system applications, consider the following features:
- IEC and IEEE compliance for power industry standards
- High EMI/EMC protection
- Redundant power supply and network backup
- Long MTBF and industrial-grade reliability
- Strong cybersecurity capabilities
Conclusion
As power systems move toward smarter, more connected grids, industrial routers have become an indispensable component of power communication infrastructure. By delivering secure, stable, and real-time connectivity, industrial routers help utilities improve operational efficiency, enhance system reliability, and support the future development of smart grids.
Investing in the right industrial router is not just a networking decision—it is a strategic step toward a more resilient and intelligent power system.