News
What Is an IP Modem?
Date:2025-12-25
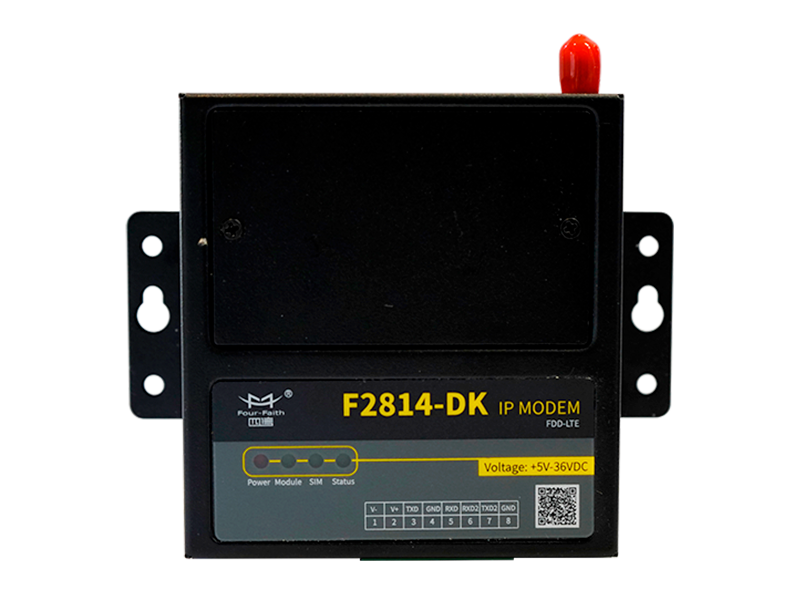
An IP modem is a communication device that enables data transmission over IP-based networks, allowing machines, sensors, or remote equipment to send and receive data using standard Internet protocols.
Unlike traditional analog modems, which convert digital signals into analog signals for phone lines, IP modems work entirely with digital data and IP networks, such as Ethernet, cellular (4G/5G), or private networks.
How Does an IP Modem Work?
An IP modem acts as a bridge between a device and an IP network.
Basic working process:
A device (such as an industrial controller, RTU, or sensor) generates data
The IP modem packages this data into IP packets
The data is transmitted over an IP network (LAN, WAN, or cellular)
The receiving system decodes the data and processes it remotely
This allows real-time or near–real-time communication between distributed systems.
Key Features of an IP Modem
Most IP modems share the following characteristics:
IP-based communication (TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, MQTT, etc.)
Remote access and monitoring
Support for wired or wireless networks
High reliability for industrial environments
Secure data transmission (VPN, encryption, authentication)
Types of IP Modems
1. Cellular IP Modems
These use mobile networks such as 4G LTE or 5G to transmit data.
Common use cases:
Remote monitoring
Smart grids
Transportation systems
Oil & gas fields
2. Ethernet IP Modems
Designed for fixed network environments using Ethernet connections.
Common use cases:
Factory automation
Building management systems
Data centers
3. Serial-to-IP Modems
These connect legacy serial devices (RS232 / RS485 / RS422) to modern IP networks.
Common use cases:
SCADA systems
Utility substations
Industrial automation upgrades
IP Modem vs Traditional Modem
| Feature | IP Modem | Traditional Modem |
| Network type | IP-based | Analog phone line |
| Data format | Digital | Analog & digital |
| Speed | High | High |
| Remote management | Yes | Limited |
| Industrial use | Very common | Rare |
Where Are IP Modems Used?
IP modems are widely used across many industries:
Power utilities – grid monitoring and protection
Industrial automation – PLC and SCADA communication
Transportation – traffic systems and fleet management
Environmental monitoring – weather stations and sensors
Smart cities – lighting, water, and infrastructure control
Benefits of Using an IP Modem
Real-time data access
Reduced operational costs
Easy system integration
Scalability for large deployments
Improved reliability and security
These benefits make IP modems a key component in modern digital infrastructure.
Choosing the Right IP Modem
When selecting an IP modem, consider:
Network type (Ethernet, 4G, 5G)
Protocol compatibility
Environmental conditions
Security requirements
Remote management capabilities
Choosing the correct model ensures long-term stability and performance.
Conclusion
An IP modem is a critical communication device that enables reliable, secure, and efficient data transmission over IP networks. As industries continue to digitalize and move toward intelligent systems, IP modems play an essential role in connecting devices, systems, and data across vast distanc